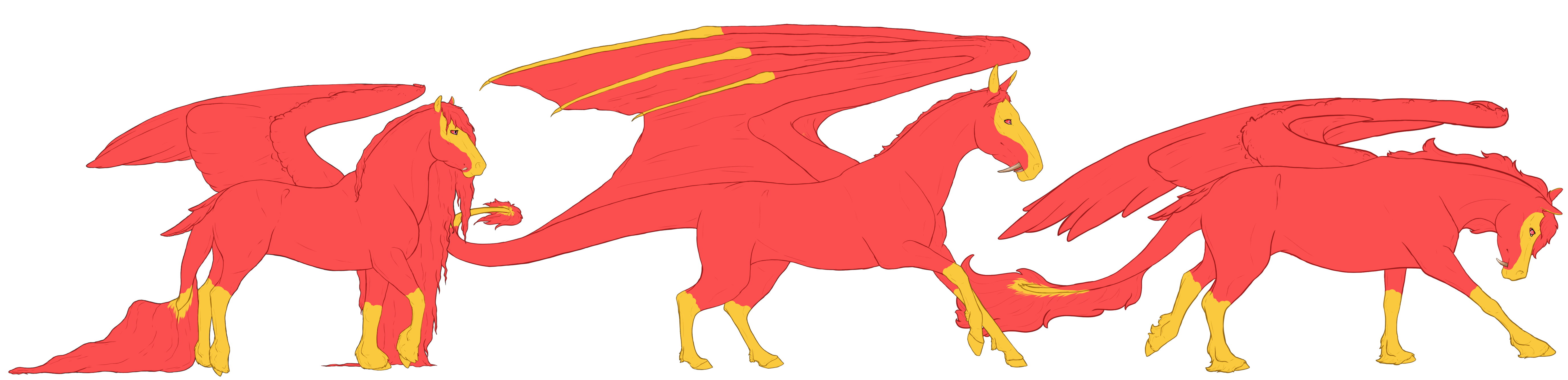
Traits
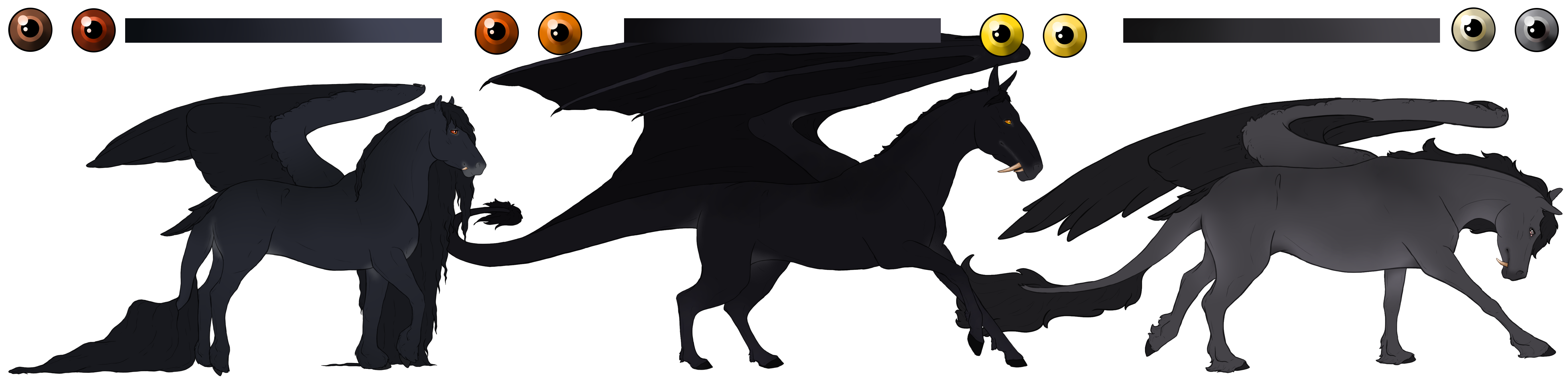
Black[E] (Free)
EE aa
Trait Count - 0
Genetic Code Variations
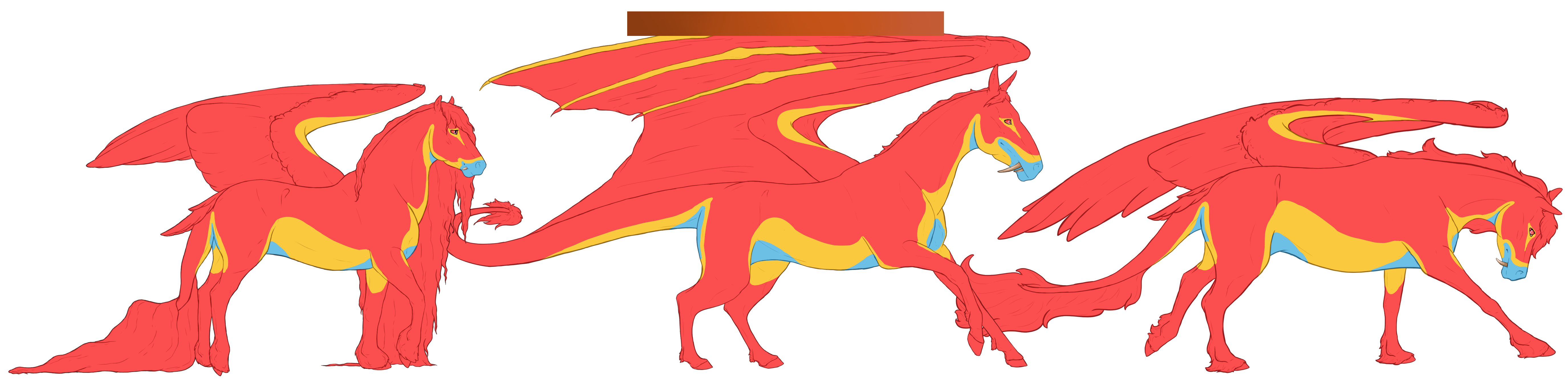
Ee aa | EE aa
Black base coats are caused by a Beatus having at least one copy of the extension(E) gene and no copies of the agouti(A) gene. This causes the coat of a Beatus to be black in color, and their skin to be varying shades of grey.
- Flight feathers and webbing will match the mane color.
- Hoof color tends to be slightly darker than the skin color.
- Dark coated blacks will always have skin and hooves lighter than their coats. Lighter coated blacks can have skin that's dark or lighter, but it will always be obviously grey and not black in color.
Eye Colors
Brown, Orange, Yellow, Grey
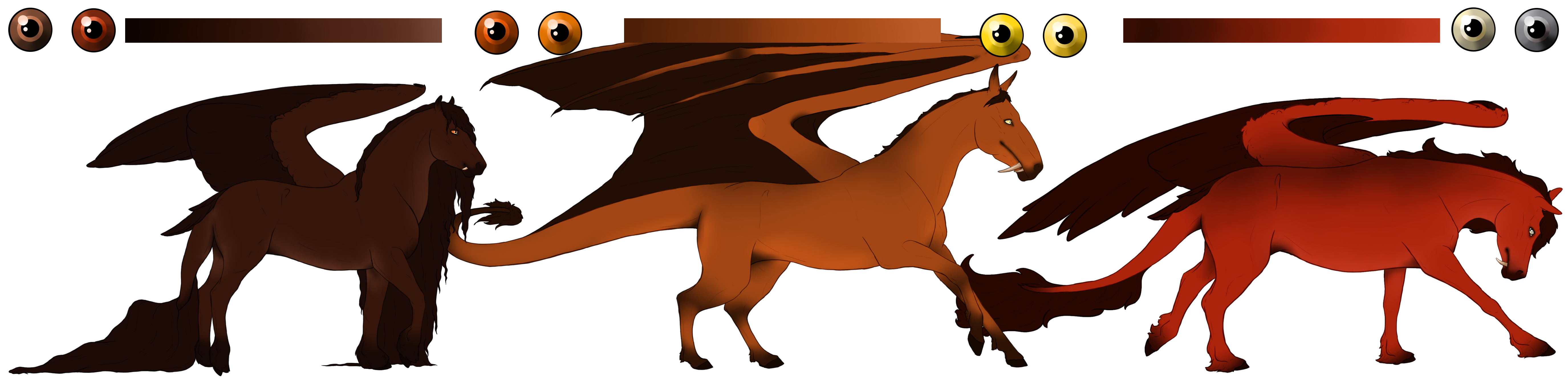
Bay[E A] (Free)
EE AA
Trait Count - 0
Genetic Code Variations
Ee Aa | EE Aa | Ee AA | EE AA | Ee AAt | EE AAt
Bay base coats are caused by a Beatus having at least one copy of the extension(E) and agouti(A) genes. The agouti gene suppresses the extension gene to expressing only on certain parts of a Beatus' body, called points.
Bay has three variants; Wild Bay(A+), Classic Bay(A), and Seal Bay(At). Wild Bay is the most dominant expression, while Seal Bay is the most recessive.
- Flight feathers and webbing will match the mane color.
- Hoof color tends to be slightly darker than the skin color.
Eye Colors
Brown, Orange, Yellow, Grey
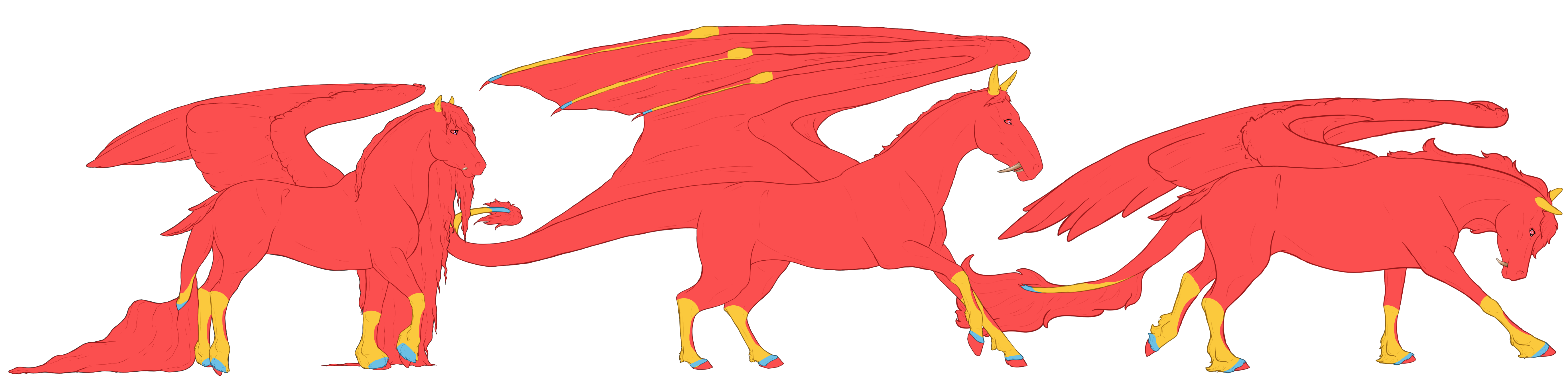
Bay Point Range
Blue is the minimum required expression
Yellow is the maximum optional expression
Red is the area expression is not allowed.
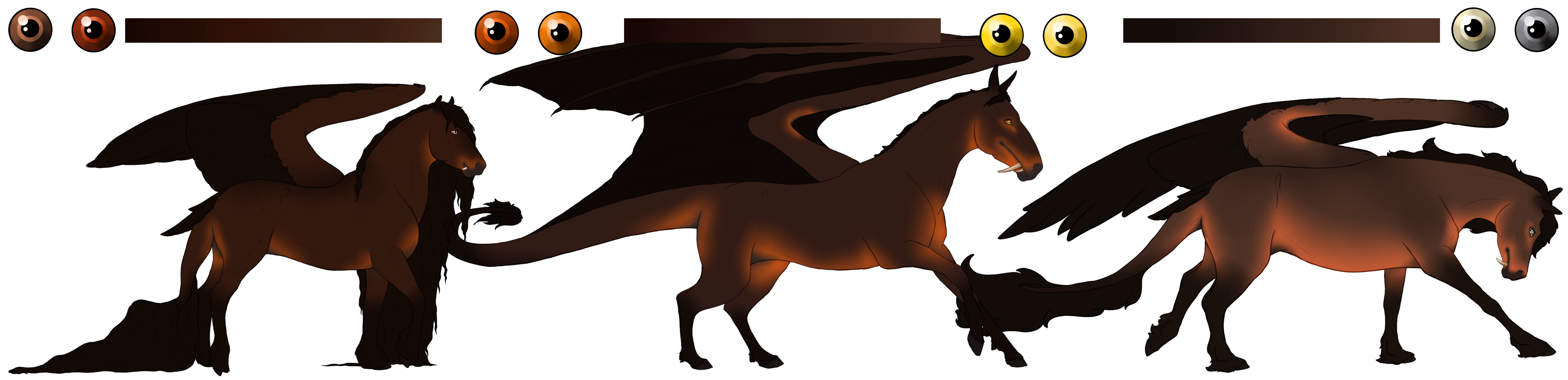
Wild Bay[E A+] (Free)
EE A+A+
Trait Count - 0
Genetic Code Variations
Ee A+a | EE A+a | Ee A+A+ | EE A+A+ | Ee A+A | EE A+A | Ee A+At | EE A+At
Bay and Bay variant base coats are caused by a Beatus having at least one copy of the extension(E) and agouti(A) genes. The agouti gene suppresses the extension gene to expressing only on certain parts of a Beatus' body, called points.
Bay has three variants; Wild Bay(A+), Classic Bay(A), and Seal Bay(At). Wild Bay is the most dominant expression of bay and highly restricts the expression of a Beatus' points. Seal Bay is the most recessive, and can sometimes be mistaken for a black Beatus.
- Flight feathers and webbing will match the mane color.
- Hoof color tends to be slightly darker than the skin color.
Eye Colors
Brown, Orange, Yellow, Grey
Wild Bay Point Range
Bay Point Range
Blue is the minimum required expression
Yellow is the maximum optional expression
Red is the area expression is not allowed.
Seal Bay[E At] (Free)
EE AtAt
Trait Count - 0
Genetic Code Variations
Ee Ata | EE Ata | Ee AtAt | EE AtAt
Bay and Bay variant base coats are caused by a Beatus having at least one copy of the extension(E) and agouti(A) genes. The agouti gene suppresses the extension gene to expressing only on certain parts of a Beatus' body, called points.
Bay has three variants; Wild Bay(A+), Classic Bay(A), and Seal Bay(At). Wild Bay is the most dominant expression of bay and highly restricts the expression of a Beatus' points. Seal Bay is the most recessive, and can sometimes be mistaken for a black Beatus.
- Flight feathers and webbing will match the mane color.
- Hoof color tends to be slightly darker than the skin color.
Eye Colors
Brown, Orange, Yellow, Grey
Seal Bay Point Range
Blue is the minimum required expression
Yellow is the maximum optional expression
Red is the area expression is not allowed.
Seal Bay Chrome Range
Blue is the minimum required expression
Yellow is the maximum optional expression
Red is the area expression is not allowed.
Chestnut[ee] (Free)
ee aa
Trait Count - 0
Genetic Code Variations
ee aa | ee A+a | ee Aa | ee Ata | ee A+A+ | ee AA | ee AtAt | ee A+A | ee A+At | ee AAt
Chestnut base coats are caused by a Beatus having no copies of the extension(E) gene. This causes the coat of a Beatus to be red in color, and their skin to be varying shades of grey. Chestnut Beatus can have any copy of the agouti(A) genes, as it does not affect their coloring.
- Flight feathers and webbing will match the mane color.
- Hoof color tends to be slightly darker than the skin color.
Eye Colors
Brown, Orange, Yellow, Grey
Free White (Free)
Free White
Facial markings can range from a tiny little star to a big apron over the face. Free white markings will not turn eye blue if they touch.
Leg markings are a bit more complex, they also have different ways they can appear.
Markings can be regular, irregular, and broken. White markings can also have ermine or distal spots. Ermine spots are a few spots on the leg markings right by the hoof, while distal markings can appear anywhere on the marking. Ermine and distal spots can also appear on facial markings, ermine will typically stick to the edge of facial markings. These spots will typically be only a handful, as to not be confused with Belton Spots.
Free White Range
Yellow is the maximum optional expression.
Red is the area expression is not allowed.